Buy Chainlink
Chainlink
LINK
Recent Trades
Past 72 hours activity| Time | Instrument | Quantity | Price | Side |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Overview
What is Chainlink?
What is Chainlink (LINK)? And how do investors buy Chainlink on CoinJar? Chainlink is a cryptocurrency that plays a crucial role in the world of decentralised finance (DeFi).
Chainlink is a decentralised oracle network that bridges the gap between smart contracts and real-world data.
Decentralised oracle networks
Smart contracts on blockchains can’t access external data directly. Chainlink solves this problem by providing a decentralised network of oracles.
These oracles gather real-world data (such as stock prices, weather conditions, or sports scores) and feed it into smart contracts.
Imagine a smart contract that triggers a payment when a specific event occurs (e.g., a flight delay). To execute this, the contract needs accurate external data. Oracles act as trusted intermediaries, ensuring that smart contracts receive reliable information. This makes it a good solution for DeFi applications.
How does Chainlink solve the Oracle Problem?
The oracle problem arises because smart contracts cannot directly access external data. Chainlink addresses this by creating an incentive system for oracles. These oracles provide reliable data, gain a positive reputation, and are rewarded with LINK tokens. As they accumulate reputation, their accuracy and reliability increase.
Is Chainlink a good investment?
Here are some factors to consider.
Real-world adoption
The technology is actively used by various projects, including DeFi platforms, gaming, and supply chain management.
White paper and vision
The white paper outlines its purpose and technical details. It’s essential reading for potential investors.
Team
Co-founded by Sergey Nazarov and Steve Ellis, both are experienced in blockchain technology.
Market demand
As blockchain networks expand, the need for reliable oracles grows. Chainlink decentralises this critical service.
Amount of LINK
Keep an eye on the circulating supply of LINK tokens. Scarcity can impact its value.

Buy using a bank transfer!
Buy Chainlink using a bank transfer. Get cash in your account with SEPA. Convert crypto-to-crypto with a single click.How to buy Chainlink with CoinJar
Start your cryptocurrency portfolio with CoinJar by following these steps.Featured In

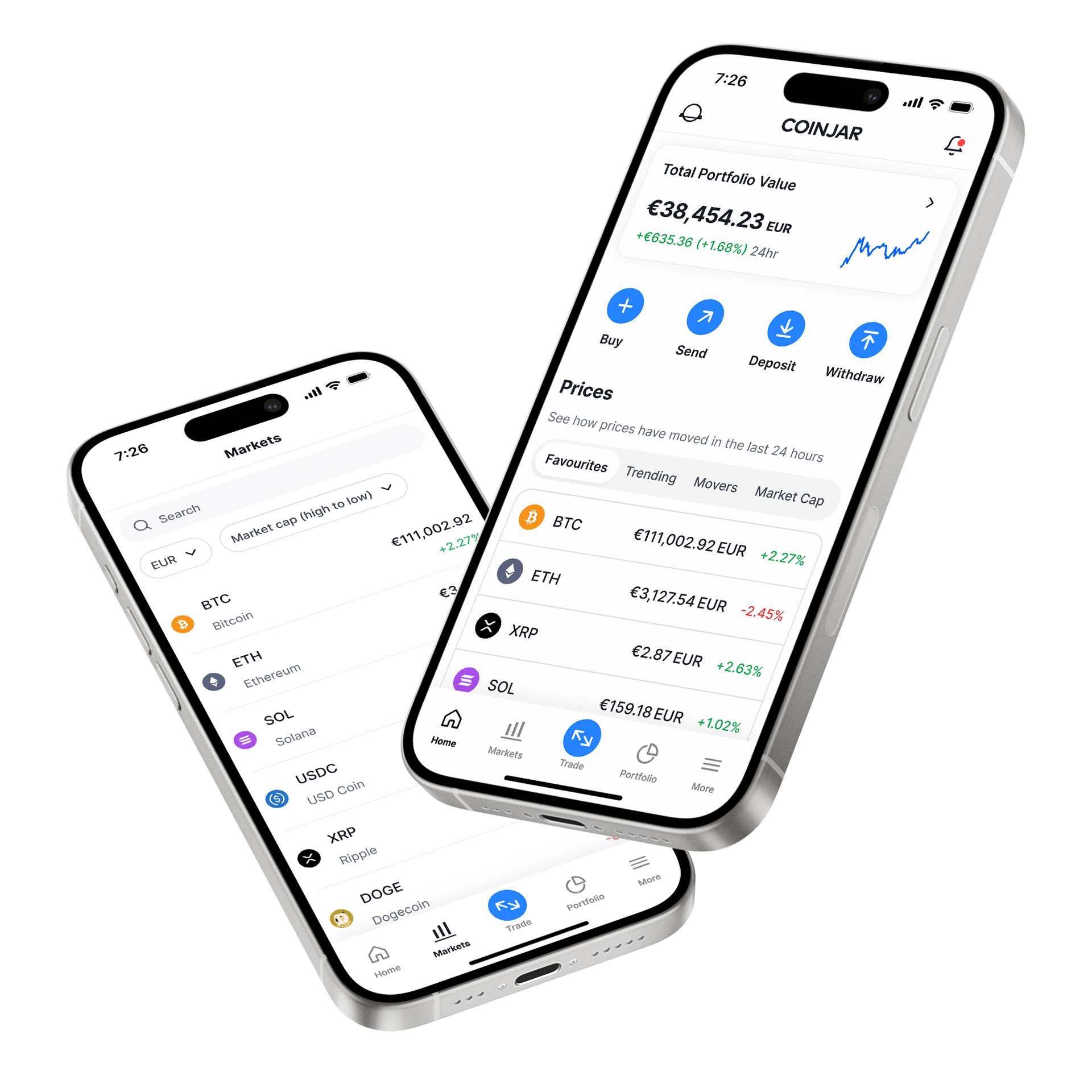
CoinJar App
All-in-one crypto wallet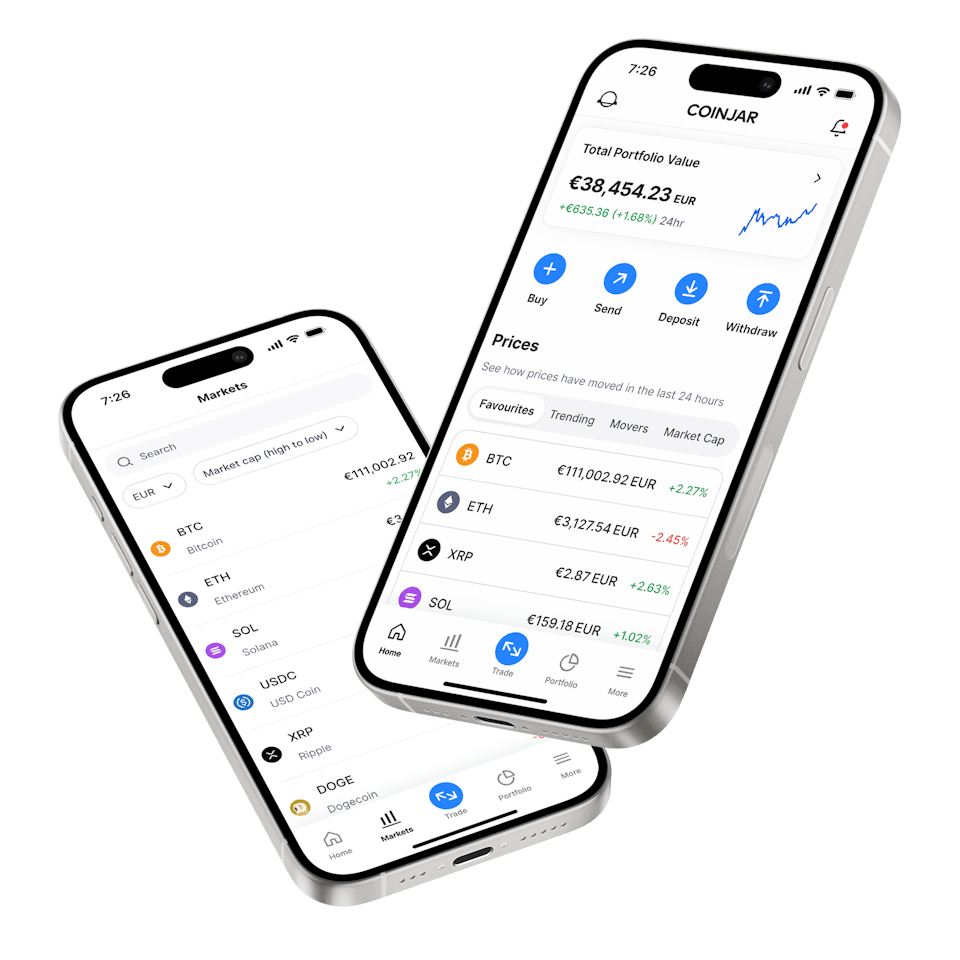
CoinJar App
All-in-one crypto wallet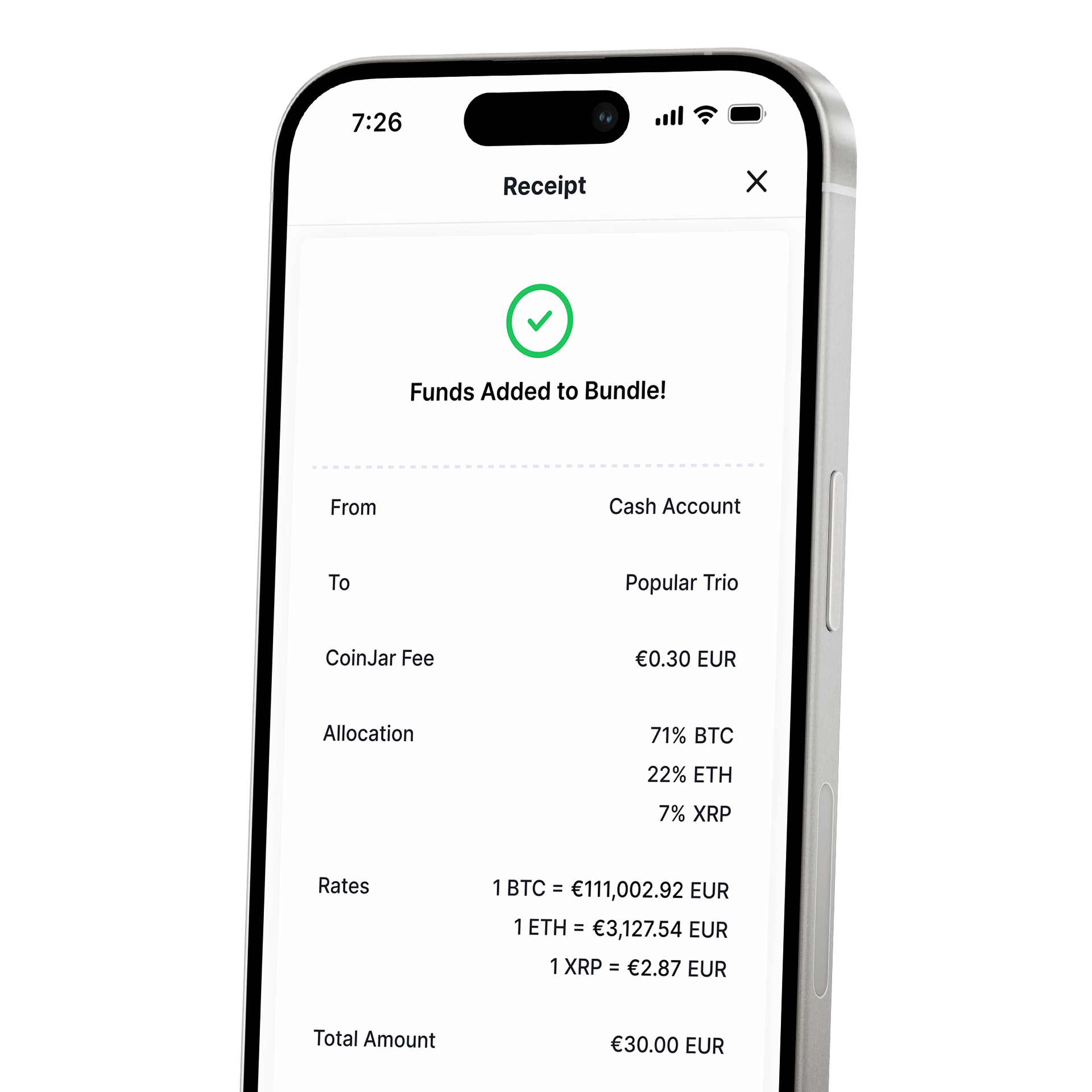
CoinJar DCA (Coming Soon) & Bundles
AUTOMATE & DIVERSIFY YOUR PORTFOLIOCoinJar DCA (Coming Soon) & Bundles
AUTOMATE & DIVERSIFY YOUR PORTFOLIO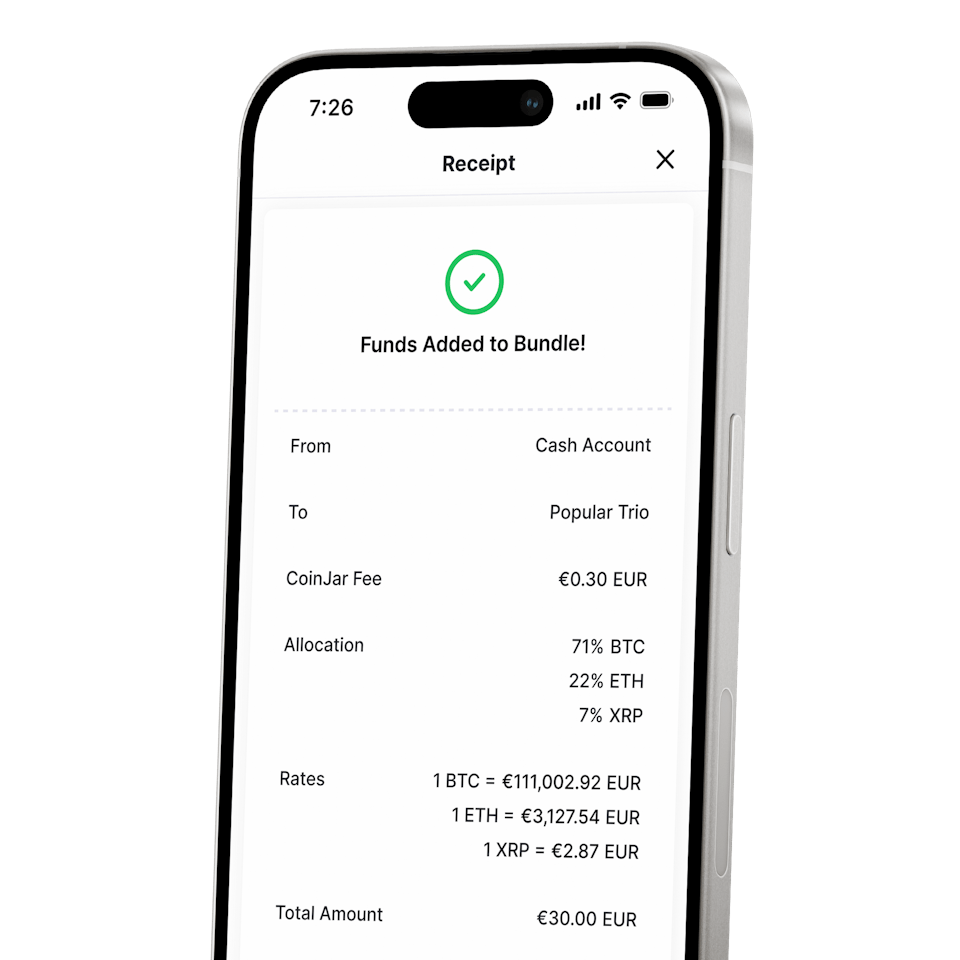
Warning: Past performance is not a reliable guide to future performance. If you invest in this product, you may lose some, or all, of the money you invest. The above information is not to be read as investment, legal or tax advice and takes no account of particular personal or market circumstances; all readers should seek independent investment, legal and tax advice before investing in cryptocurrencies. There are no government or central bank guarantees in the event something goes wrong with your investment. This information is provided for general information and/or educational purposes only. No responsibility or liability is accepted for any errors of fact or omission expressed therein. CoinJar Europe Limited makes no representation or warranty of any kind, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, validity, reliability, availability, or completeness of any such information. CoinJar Europe Limited is authorised by the Central Bank of Ireland as a crypto-asset service provider (registration number C496731).
Your information is handled in accordance with CoinJar’s Privacy Policy.
Warning: Past performance is not a reliable guide to future performance. If you invest in this product, you may lose some, or all, of the money you invest. The above information is not to be read as investment, legal or tax advice and takes no account of particular personal or market circumstances; all readers should seek independent investment, legal and tax advice before investing in cryptocurrencies. There are no government or central bank guarantees in the event something goes wrong with your investment. This information is provided for general information and/or educational purposes only. No responsibility or liability is accepted for any errors of fact or omission expressed therein. CoinJar Europe Limited makes no representation or warranty of any kind, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, validity, reliability, availability, or completeness of any such information.
CoinJar Europe Limited is authorised by the Central Bank of Ireland as a crypto-asset service provider (registration number C496731).
For more information on our regulatory status and the crypto-asset services we are authorised to provide, please see our official announcement and our MiCAR Legal & Regulatory Information page.
Apple Pay and Apple Watch are trademarks of Apple Inc. Google Pay is a trademark of Google LLC.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.