Buy Ethereum Classic
Ethereum Classic
ETC
What is Ethereum Classic?
How to buy Ethereum Classic (ETC). What is ETC? It is a smart contract network, where developers build and run apps (called dApps, which are apps built on the blockchain rather than on the internet). The native token of this network is ETC.
Let’s break it down.
Understanding Ethereum Classic (ETC)
The origins: Ethereum Classic’s birth
Ethereum Classic was born in 2016 as a result of a significant event in the crypto world. To understand it, we need to rewind a bit.
The DAO hack
Imagine a digital organisation called The DAO (Decentralised Autonomous Organisation).
It was like a venture capital fund run by code on the Ethereum blockchain. People invested their money in The DAO, hoping for positive investment returns. But then, disaster struck! A hacker exploited a flaw in The DAO’s smart contract and drained a massive amount of Ether (ETH).
The great divide
The Ethereum community faced a dilemma. Should they reverse the hack and return the stolen funds (like hitting the “undo” button)? Or should they stick to the principle that “Code is Law,” meaning that once a smart contract executes, its outcome is final?
The split
The community split into two camps: Majority Opinion and the Rebels.
Majority opinion
Most people chose to reverse the hack, creating a new version of Ethereum (which we now know as Ethereum or ETH).
The rebels
A smaller group believed in the original Ethereum vision. They stood by the unaltered history and the Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus mechanism. This group became Ethereum Classic (ETC).
What makes Ethereum Classic unique?
Code Is Law
ETC sticks to the idea that smart contracts are like legal contracts. Once they execute, there’s no turning back. If you invest in a flawed project, you bear the consequences.
Decentralised governance
ETC’s smart contracts operate without intermediaries. No lawyers, no judges — just code. If conditions are met, the contract self-executes. If not, penalties apply.
Blockchain twins
Think of Ethereum as the older twin and Ethereum Classic as the younger one. They share DNA (the same codebase) but have different personalities. ETC retains the original Ethereum blockchain, while ETH has moved to Proof-of-Stake (PoS).
Smart contracts
What Are Smart Contracts? Imagine if contracts could execute themselves. They automatically enforce agreements when specific conditions are met.
Here are some everyday examples. Take real estate for example.
If the buyer pays the deposit by a certain date, the contract proceeds. No lawyers are needed, the code does the job.
Smart contracts live on a distributed ledger (a fancy term for a shared database). No central authority controls them. They’re immutable and transparent.
Conclusion: Ethereum Classic
Ethereum Classic is like the rebel sibling. It clings to the original Ethereum principles, even when the majority went a different way.
So, next time you hear about ETC, remember, it’s the blockchain that believes in “Code is Law.”







Cash, credit or crypto?
Buy Ethereum Classic using Visa or Mastercard. Get cash in your account with Faster Payments Service (FPS). Convert crypto-to-crypto with a single click.How to buy Ethereum Classic with CoinJar
Start your cryptocurrency portfolio with CoinJar by following these steps.
Finder Awards Winner 2024
CRYPTO TRADING - VALUEFinder Awards Winner 2024
CRYPTO TRADING - VALUE
Featured In

CoinJar App
All-in-one crypto walletCoinJar App
All-in-one crypto wallet
CoinJar Exchange
FOR PROFESSIONAL CRYPTO TRADERS
CoinJar Exchange
FOR PROFESSIONAL CRYPTO TRADERS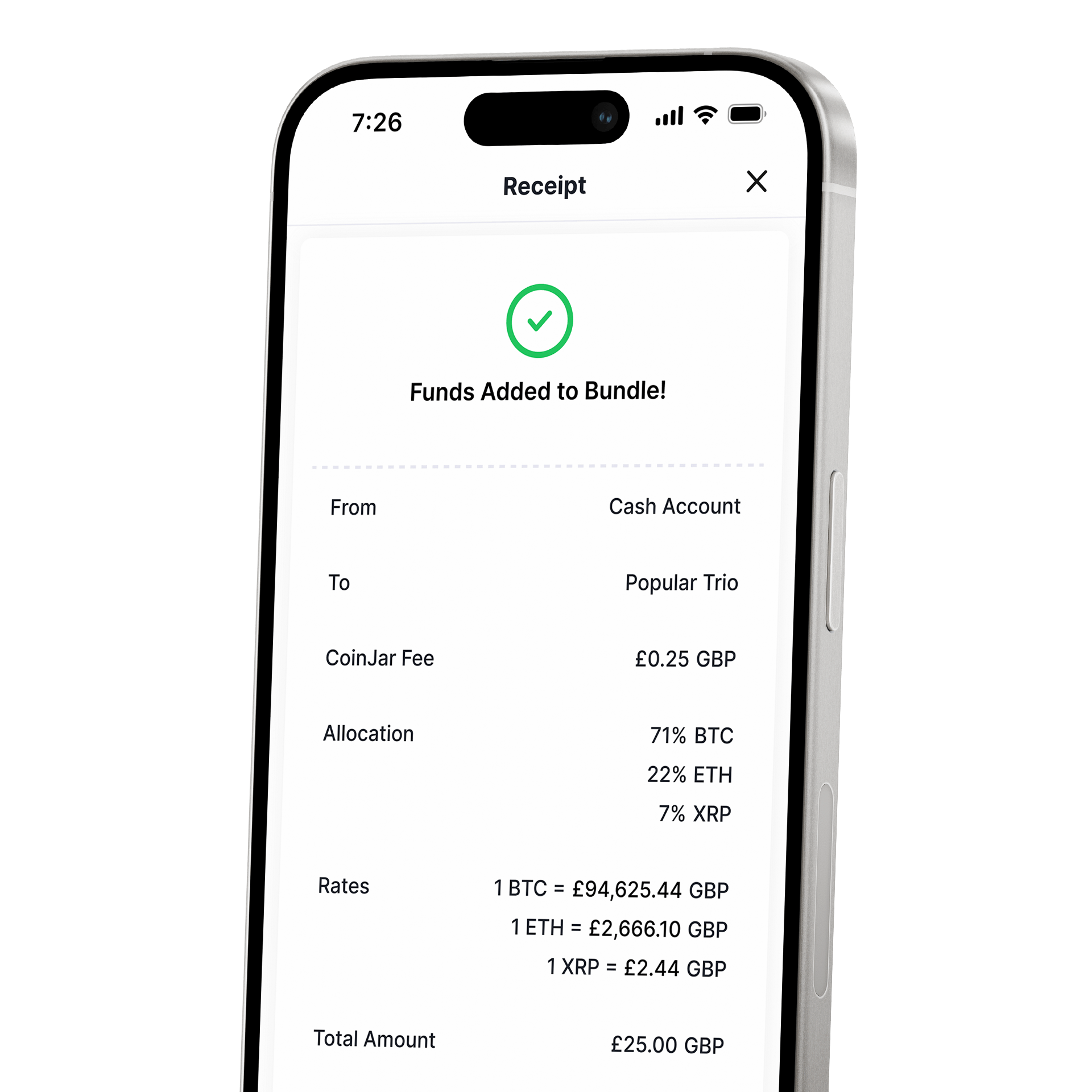
CoinJar DCA & Bundles
AUTOMATE & DIVERSIFY YOUR PORTFOLIOCoinJar DCA & Bundles
AUTOMATE & DIVERSIFY YOUR PORTFOLIO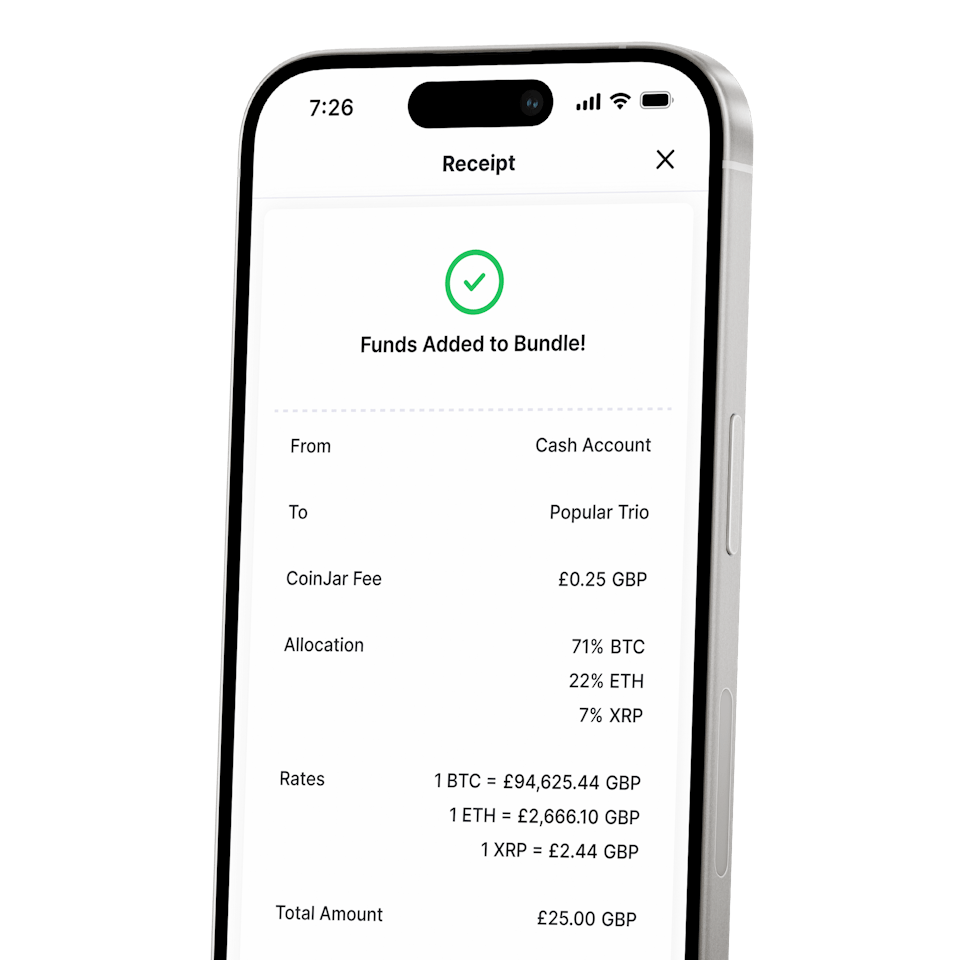
Standard Risk Warning: The above article is not to be read as investment, legal or tax advice and it takes no account of particular personal or market circumstances; all readers should seek independent investment advice before investing in cryptocurrencies.
The article is provided for general information and educational purposes only, no responsibility or liability is accepted for any errors of fact or omission expressed therein. Past performance is not a reliable indicator of future results.
We use third party banking, safekeeping and payment providers, and the failure of any of these providers could also lead to a loss of your assets. We recommend you obtain financial advice before making a decision to use your credit card to purchase cryptoassets or to invest in cryptoassets. Capital Gains Tax may be payable on profits.
CoinJar's digital currency exchange services are operated in the UK by CoinJar UK Limited (company number 8905988), registered by the Financial Conduct Authority as a Cryptoasset Exchange Provider and Custodian Wallet Provider in the United Kingdom under the Money Laundering, Terrorist Financing and Transfer of Funds (Information on the Payer) Regulations 2017, as amended (Firm Reference No. 928767). In the UK, it's legal to buy, hold, and trade crypto, however cryptocurrency is not regulated in the UK.
It's vital to understand that once your money is in the crypto ecosystem, there are no rules to protect it, unlike with regular investments. You should not expect to be protected if something goes wrong. So, if you make any crypto-related investments, you're unlikely to have recourse to the Financial Services Compensation Scheme (FSCS) or the Financial Ombudsman Service (FOS) if something goes wrong.
The performance of most cryptocurrency can be highly volatile, with their value dropping as quickly as it can rise. Past performance is not an indication of future results. Remember: Don't invest unless you're prepared to lose all the money you invest. This is a high-risk investment and you should not expect to be protected if something goes wrong. Take 2 mins to learn more at: https://www.coinjar.com/uk/risk-summary.
UK residents are required to complete an assessment to show they understand the risks associated with what crypto/investment they are about to buy, in accordance with local legislation. Additionally, they must wait for a 24-hour "cooling off" period, before their account is active, due to local regulations. If you use a credit card to buy cryptocurrency, you would be putting borrowed money at a risk of loss.
We recommend you obtain financial advice before making a decision to use your credit card to purchase cryptoassets or to invest in cryptoassets.
Specific risks associated with DeFi tokens Decentralised Finance (or 'DeFi') tokens (e.g. UNI, AAVE) are crypto-assets linked to financial applications and protocols built on decentralised blockchain technology. DeFi tokens carry the following risks:
Smart contract risk: DeFi relies heavily on smart contracts. Even a minor coding error or oversight can lead to a contract being exploited, potentially resulting in significant losses for DeFi tokens.
Regulatory risk: DeFi operates in a decentralised manner, often without intermediaries or financial crime controls. Regulatory bodies across jurisdictions might introduce new regulations impacting the use, value, or legality of certain DeFi protocols or assets.
Rug-pulls / Exit scams: Some DeFi projects might be launched by anonymous or pseudonymous teams, increasing the risk of "rug pulls" where developers abandon the project and withdraw funds, leaving investors with worthless tokens.
Data/oracle risk: DeFi protocols often rely on external data sources or 'oracles. Manipulation or inaccuracies in these data sources can lead to unintended financial outcomes within the protocols. Protocol complexity: The complexity of some DeFi protocols can make it difficult for average users to fully understand the mechanisms and associated risks.
Specific risks associated with meme coins:
'Meme coins' (e.g. DOGE, SHIB, PEPE) are crypto-assets whose value is driven primarily by community interest and online trends.
Meme coins carry the following risks:
Volatility risk: Meme coins can have extreme price volatility, often experiencing rapid and unpredictable price fluctuations within short periods. The value of meme coins can be influenced by social media trends, celebrity endorsements, and other factors unrelated to traditional investment fundamentals. Lack of utility: Meme coins often lack intrinsic value or utility, being primarily driven by community interest, online trends, and speculative trading.
Market manipulation: Meme coins may be susceptible to increased risk of market manipulation including 'pump-and-dump' schemes, where the price is artificially inflated followed by a sudden crash.
Lack of transparency: Meme coins may have limited available information about their development teams, goals, and financials. This lack of transparency can make it challenging to assess the credibility and potential of a meme coin accurately.
Emotional investing: Meme coins often garner strong emotional reactions from investors, leading to impulsive decisions. Emotional trading activity can amplify losses.
Specific risks associated with stablecoins:
There is a risk that any particular stablecoin may not hold their value as against any fiat currency; or may not hold their value as against any other asset. Stablecoins carry the following risks:
Depegging events: Depegging events may occur with stablecoins that fail to maintain adequate controls and risk mitigants. A depegging event is when the value of the stablecoin no longer matches the value of the underlying asset. This could result in a loss of some or all of your investment.
Counterparty risk: Counterparty risk arises when an asset is backed by collateral, involving a third party maintaining the collateral, which introduces risk if the party becomes insolvent or fails to maintain it.
Redemption risk: Redemption risk refers to the possibility that an asset's ability to be redeemed for underlying collateral may not be as anticipated during market fluctuations or operational issues.
Collateral risk: Collateral risk refers to the possibility of the collateral's value declining or becoming volatile, potentially impacting the asset's stability, particularly when it is another crypto-asset.
Exchange rate fluctuations: Stablecoins, often denominated in US Dollars, expose investors to fluctuations in the USD:GBP exchange rate. Algorithmic risk: Algorithm risk refers to the possibility of an asset's stability being compromised due to unexpected failure or behaviour of the underlying algorithm, potentially leading to loss of value.
CoinJar does not endorse the content of, and cannot guarantee or verify the safety of any third-party websites. Visit these websites at your own risk.
Your information is handled in accordance with CoinJar’s Privacy Policy.
Cryptoassets traded on CoinJar UK Limited are largely unregulated in the UK, and you are unable to access the Financial Service Compensation Scheme or the Financial Ombudsman Service.
We use third party banking, safekeeping and payment providers, and the failure of any of these providers could also lead to a loss of your assets.
We recommend you obtain financial advice before making a decision to use your credit card to purchase cryptoassets or to invest in cryptoassets. Capital Gains Tax may be payable on profits.
CoinJar’s digital currency exchange services are operated in the UK by CoinJar UK Limited (company number 8905988), registered by the Financial Conduct Authority as a Cryptoasset Exchange Provider and Custodian Wallet Provider in the United Kingdom under the Money Laundering, Terrorist Financing and Transfer of Funds (Information on the Payer) Regulations 2017, as amended (Firm Reference No. 928767).
Apple Pay and Apple Watch are trademarks of Apple Inc. Google Pay is a trademark of Google LLC.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.