Don’t invest unless you’re prepared to lose all the money you invest. This is a high‑risk investment and you should not expect to be protected if something goes wrong.
Buy Ethereum Name Service (ENS) in UK With GBP | CoinJar
Ethereum Name Service
ENS
Overview
What is Ethereum Name Service?
How to Buy Ethereum Name Service (ENS): Why do investors buy ENS? Because ENS simplifies crypto addresses for everyone. Let’s break it down.
What is ENS?
The Ethereum Name Service (ENS) is a distributed technology based on the blockchain. Its mission is to provide an elegant solution to the long and confusing crypto addresses we encounter in the world of cryptocurrencies.
Think of ENS as a way to create a human-readable name that represents your address, similar to a website domain or an email address.
What is the ENS token? (ENS)
The Ethereum Name Service (ENS) token (or crypto) is built on the ERC-20 standard and serves as a governance token within the ENS community. Its primary purpose is to enable community members to propose and vote on changes within the .
The of ENS tokens is capped at 100 million. Currently, 31.2 million tokens are in circulation (as at 14 May 2024).
Why is ENS useful?
Human-readable names
Cryptocurrency addresses are typically a string of random characters (like 0x98...674). Remembering or sharing these addresses can be challenging. ENS allows you to create a custom name (e.g., nick.eth) that maps to your actual crypto address. Now you can share your ENS name instead of the complex address, making transactions convenient and more intuitive.
One name for all chains
With ENS, you can use the same name across different blockchains. No more copying and pasting lengthy addresses! Whether you’re receiving Ethereum, tokens, or NFTs, your ENS name covers it all.
Decentralised websites
ENS also enables censorship-resistant, decentralised websites. By uploading your website to the InterPlanetary File System (IPFS) and associating it with your ENS name, you create a user-friendly way to access your content. Imagine browsing websites like “mywebsite.eth” instead of IPFS hashes!
How does ENS work?
Registering an ENS name
Users can register ENS names through various wallets and services. Choose a unique name (e.g., your nickname or brand) and link it to your crypto address.
Resolving ENS names
When someone enters an ENS name (e.g., “alice.eth”), the ENS system translates it into the corresponding crypto address (e.g., 0x...).
This resolution happens behind the scenes, making it seamless for users.
Integration with wallets and services
ENS is widely integrated into wallets, browsers, and apps. You can use your ENS name across platforms, simplifying transactions and interactions.
The future of ENS
ENS simplifies crypto addresses by replacing them with user-friendly names, making transactions more intuitive. For example, instead of sharing a lengthy address like “0xDC25E998338AF3F5B8A1862ADA83795FBA2D695E,” you can use a more logical format like “CoinJar.eth.”
As blockchain adoption grows, ENS will play an essential role in making crypto more accessible. Imagine a world where sending funds is as convenient as typing a friend’s name! ENS could theoretically increase in popularity and expand to support more chains, enhance protection, and become a standard part of the crypto experience.
ENS bridges the gap between complex crypto addresses and human-friendly names, making the decentralised world more user-friendly.








Cash, credit or crypto?
Buy Ethereum Name Service using Visa or Mastercard. Get cash in your account with Faster Payments Service (FPS). Convert crypto-to-crypto with a single click.How to buy Ethereum Name Service with CoinJar
Start your cryptocurrency portfolio with CoinJar by following these steps.Finder Awards Winner 2023
CRYPTO TRADING - VALUE
Featured In

CoinJar App
All-in-one crypto wallet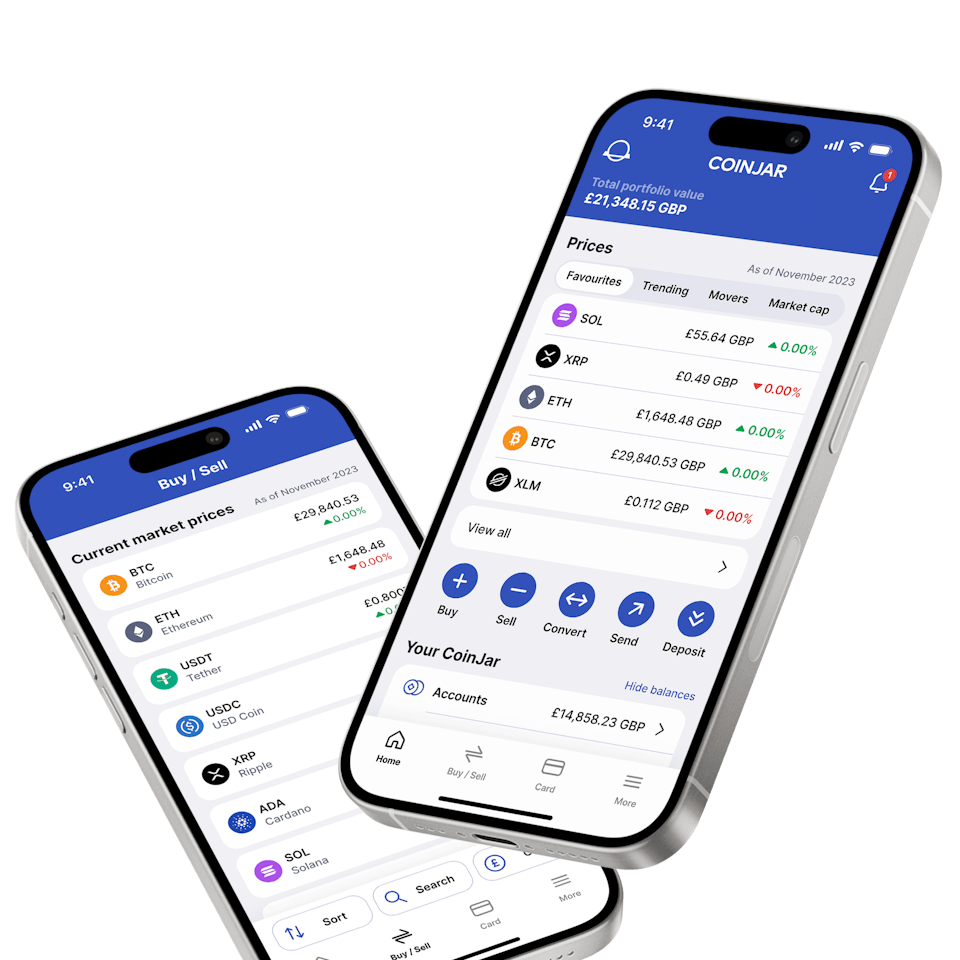
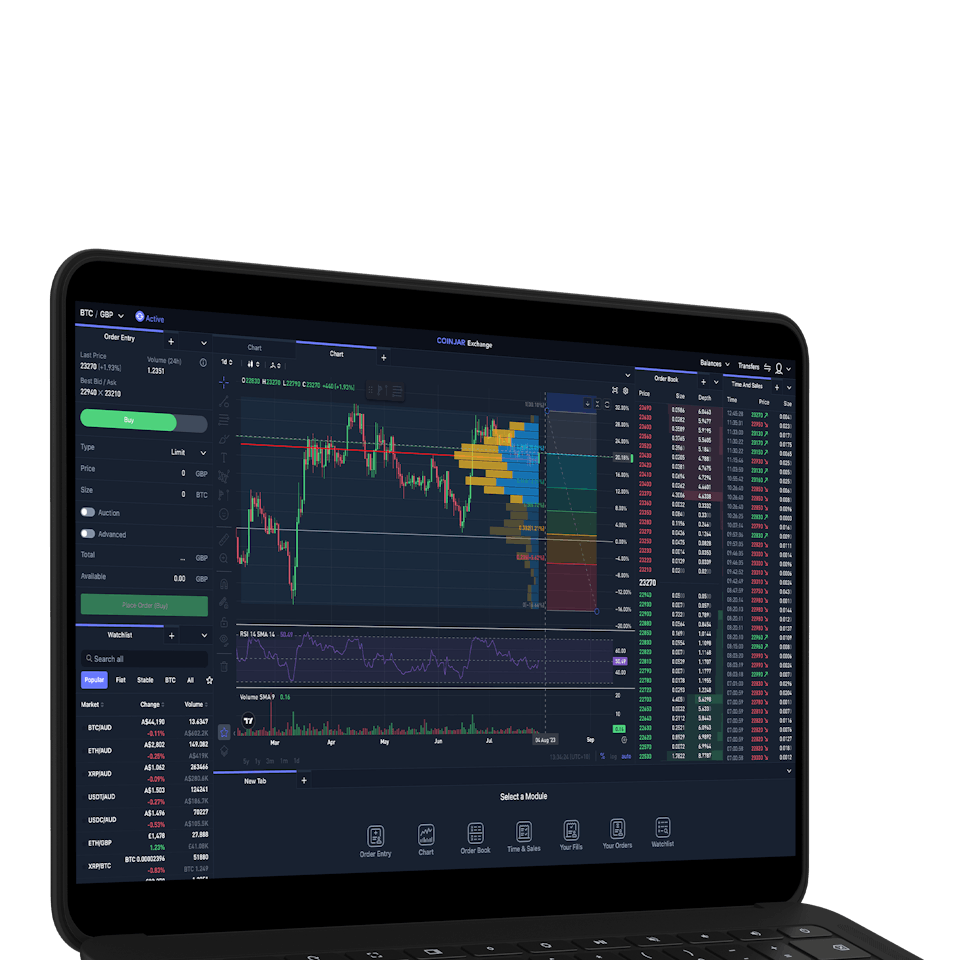
CoinJar Exchange
FOR PROFESSIONAL CRYPTO TRADERSCoinJar DCA & Bundles
AUTOMATE & DIVERSIFY YOUR PORTFOLIO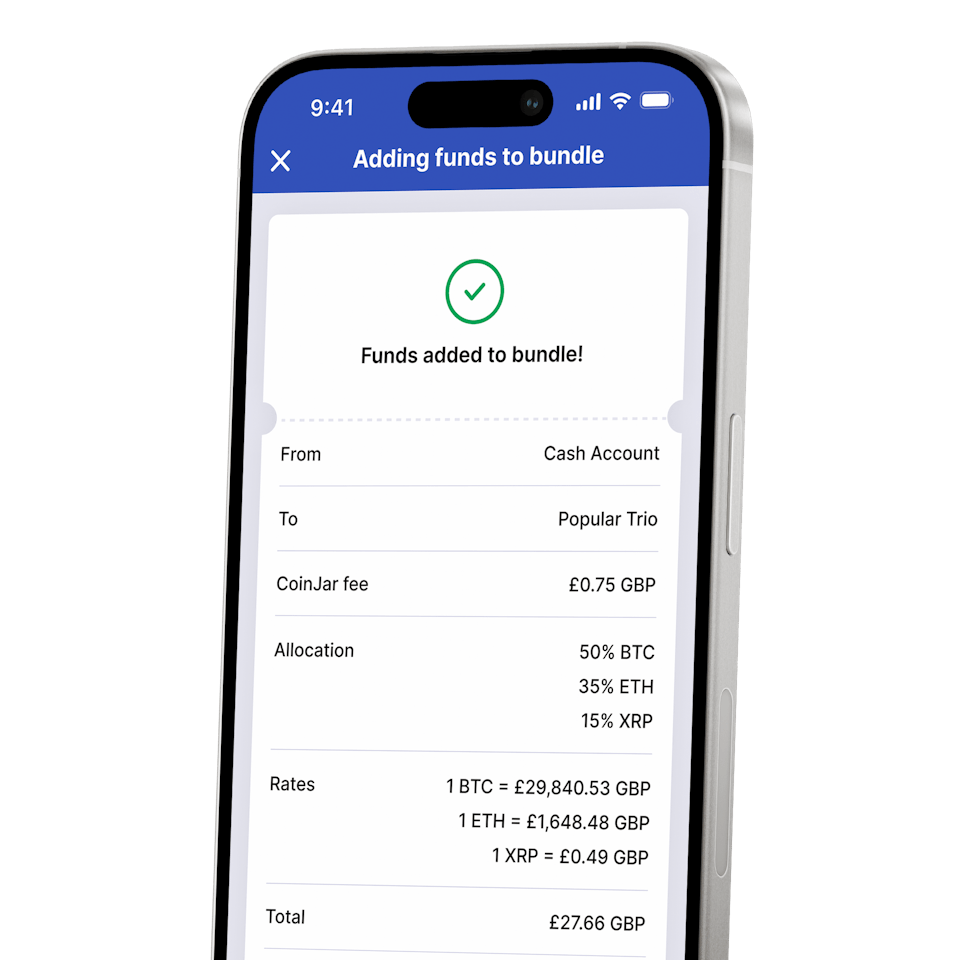
Frequently asked questions
What is ENS (Ethereum Name Service)?
ENS is a decentralised system built on the Ethereum blockchain that allows users to replace complex crypto addresses with human-readable names. It’s like a domain name service (DNS) for the Ethereum ecosystem.







Cryptoassets traded on CoinJar UK Limited are largely unregulated in the UK, and you are unable to access the Financial Service Compensation Scheme or the Financial Ombudsman Service.
We use third party banking, safekeeping and payment providers, and the failure of any of these providers could also lead to a loss of your assets. We recommend you obtain financial advice before making a decision to use your credit card to purchase cryptoassets or to invest in cryptoassets. Capital Gains Tax may be payable on profits.
CoinJar’s digital currency exchange services are operated in the UK by CoinJar UK Limited (company number 8905988), registered by the Financial Conduct Authority as a Cryptoasset Exchange Provider and Custodian Wallet Provider in the United Kingdom under the Money Laundering, Terrorist Financing and Transfer of Funds (Information on the Payer) Regulations 2017, as amended (Firm Reference No. 928767).
Apple Pay and Apple Watch are trademarks of Apple Inc. Google Pay is a trademark of Google LLC.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the and apply.

