CoinJar
Buy Bitcoin and Crypto
Sign up to buy multiple cryptocurrencies. Start investing with €10.
How to buy cryptocurrency with CoinJar
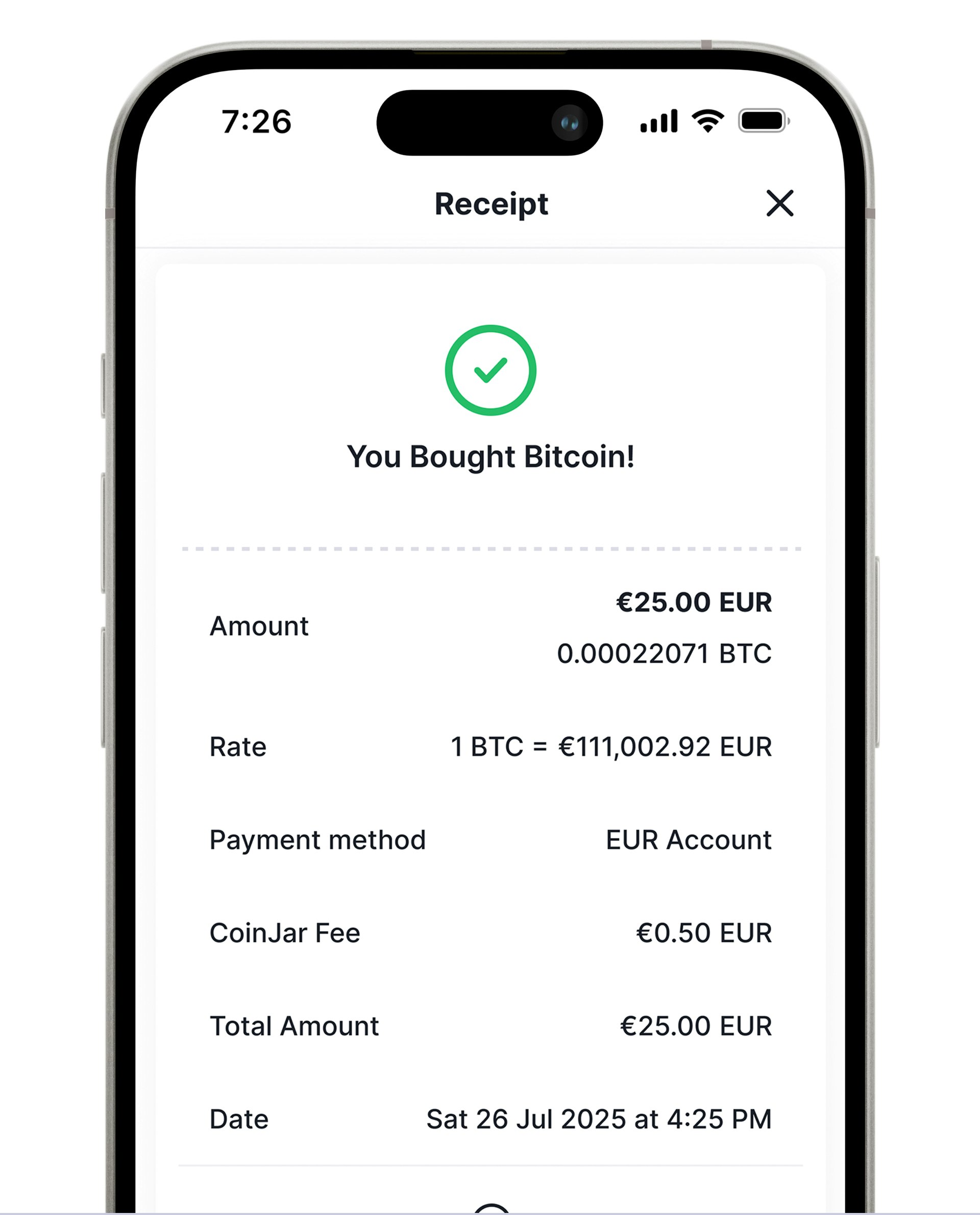
Pick your crypto
Choose between leading cryptocurrencies on CoinJar.Pay your way
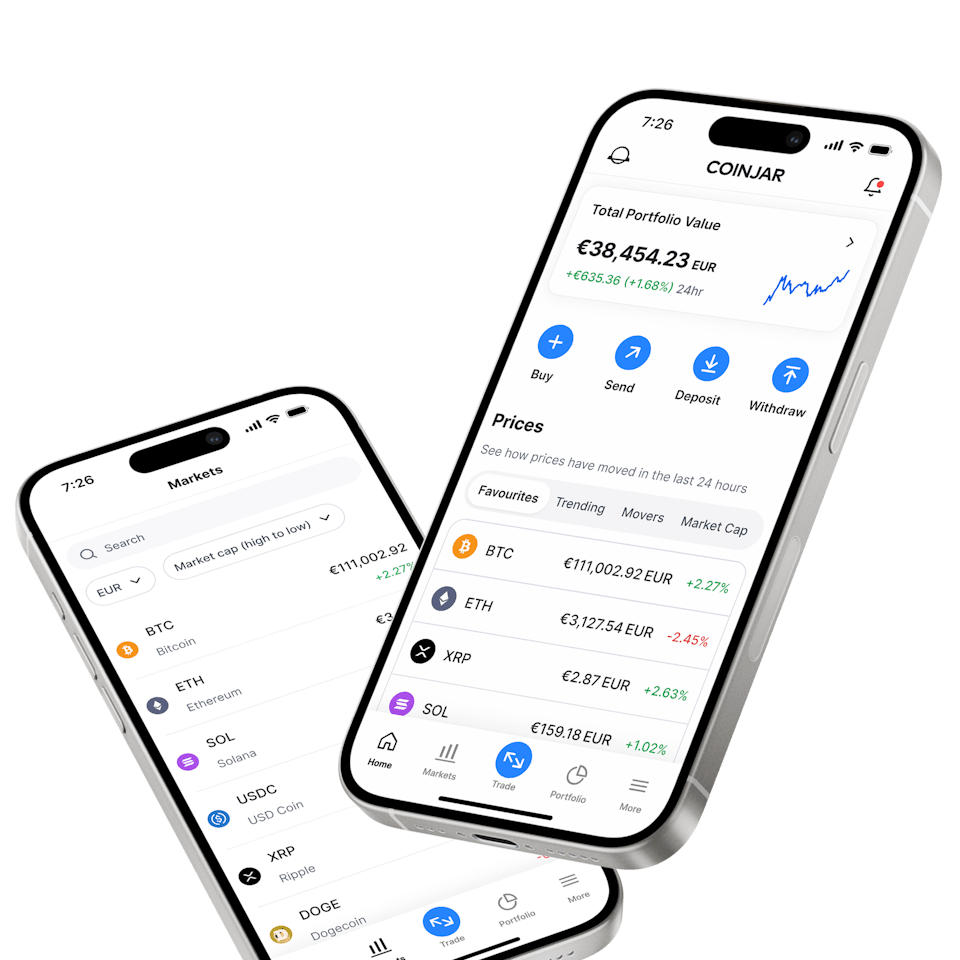
Deposit EUR via bank transfer (SEPA)Grow your portfolio
Store your crypto in our wallet. Diversify with CoinJar Bundles.



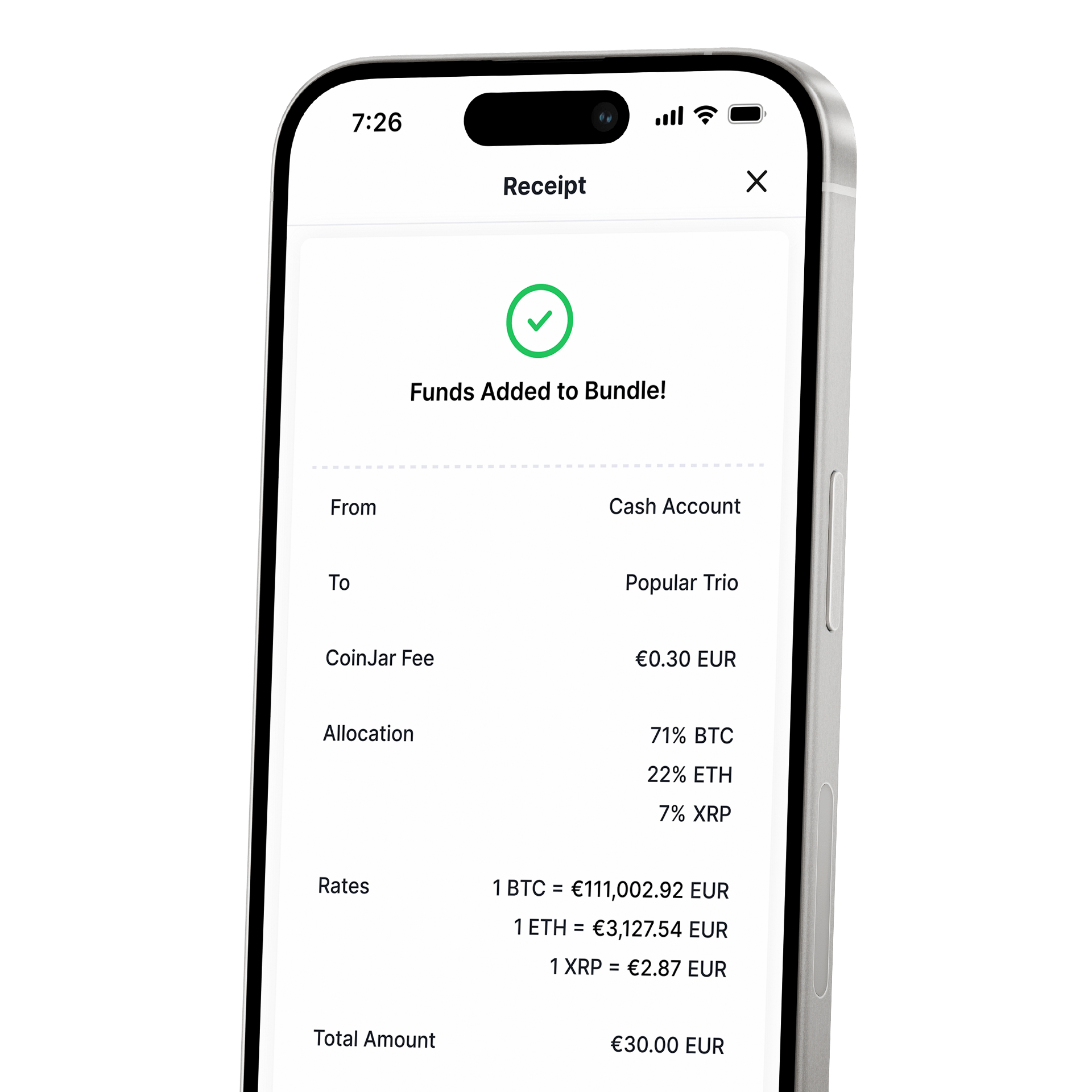
CoinJar DCA (Coming Soon) & Bundles
Automate and diversify your portfolioCoinJar DCA (Coming Soon) & Bundles
Automate and diversify your portfolio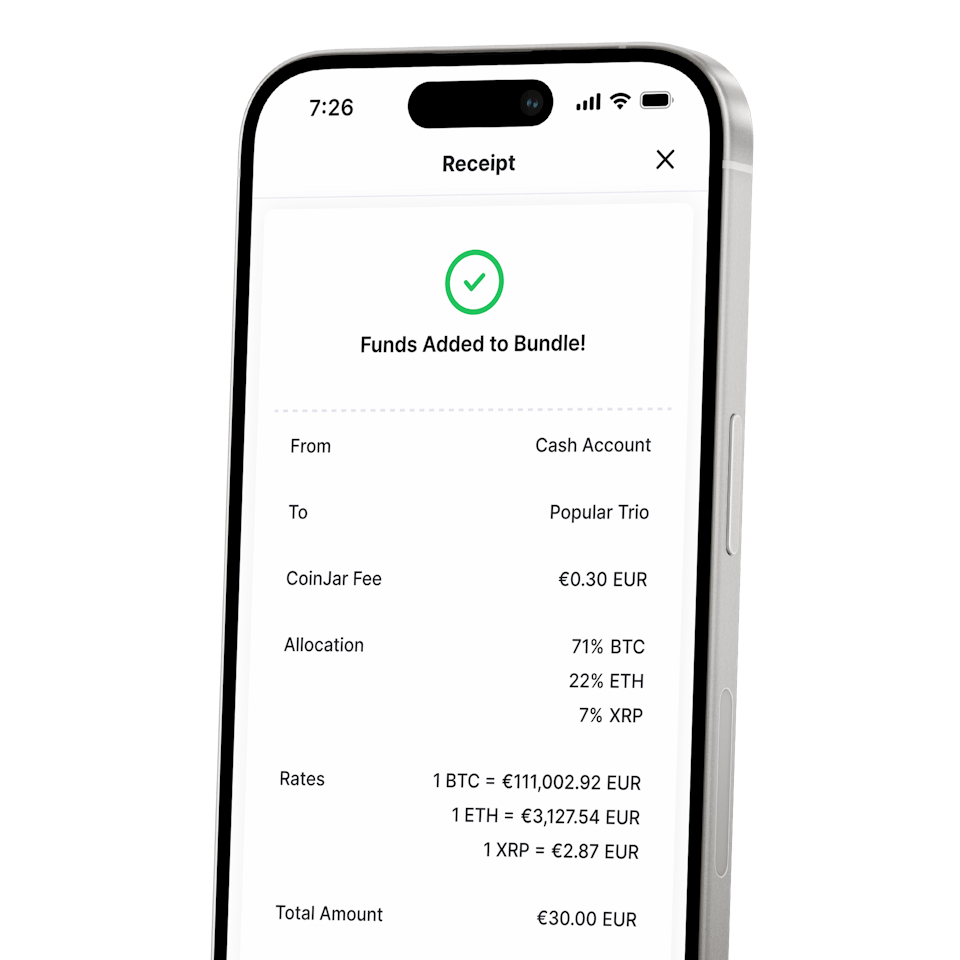
CoinJar OTC
The confidence of using a six-star white-glove service where the trades are done for you.Private and encrypted crypto storage

Fraud protection
We employ multi-level data encryption, audits and follow best practice guidelines to protect customer accounts. Our Support team uses advanced machine learning to recognise suspicious logins, account takeovers and financial fraud.
Crypto storage
Customer assets are held in custody by CoinJar Europe Limited using Fireblocks' secure wallet infrastructure as a technology provider.
Established in 2013
CoinJar was established in 2013. We’re backed by investors, which include Blackbird and DCG Group.Featured In


Your information is handled in accordance with CoinJar’s Privacy Policy.
Warning: Past performance is not a reliable guide to future performance. If you invest in this product, you may lose some, or all, of the money you invest. The above information is not to be read as investment, legal or tax advice and takes no account of particular personal or market circumstances; all readers should seek independent investment, legal and tax advice before investing in cryptocurrencies. There are no government or central bank guarantees in the event something goes wrong with your investment. This information is provided for general information and/or educational purposes only. No responsibility or liability is accepted for any errors of fact or omission expressed therein. CoinJar Europe Limited makes no representation or warranty of any kind, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, validity, reliability, availability, or completeness of any such information.
CoinJar Europe Limited is authorised by the Central Bank of Ireland as a crypto-asset service provider (registration number C496731).
For more information on our regulatory status and the crypto-asset services we are authorised to provide, please see our official announcement and our MiCAR Legal & Regulatory Information page.
Apple Pay and Apple Watch are trademarks of Apple Inc. Google Pay is a trademark of Google LLC.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

